Business Process Modelling Meaning

Imagine if you could instantly spot inefficiencies, reduce costs, and boost team performance—all by simply looking at a clear visual of your daily operations. That’s the power behind Business Process Modelling.
In this guide, we’ll explain the meaning of Business Process Modelling, why it matters, the techniques involved, and real-world examples of its application.
Understanding Business Process Modelling Meaning
Understanding what Business Process Modelling entails is the first step toward improving how work is performed in an organization. BPM provides a systematic way to visualize operations and identify how tasks, decisions, and interactions unfold.
Business Process Modelling is a method used to create a structured and graphical depiction of business operations. It typically involves charting workflows to gain insight into how tasks are performed, who performs them, and how different elements interact. BPM is not just about documentation—it serves as a foundation for process improvement, automation, and compliance.
The main goal of business process modelling is to ensure organizational processes are efficient, transparent, and aligned with business goals.
Why is Business Process Modelling Important?
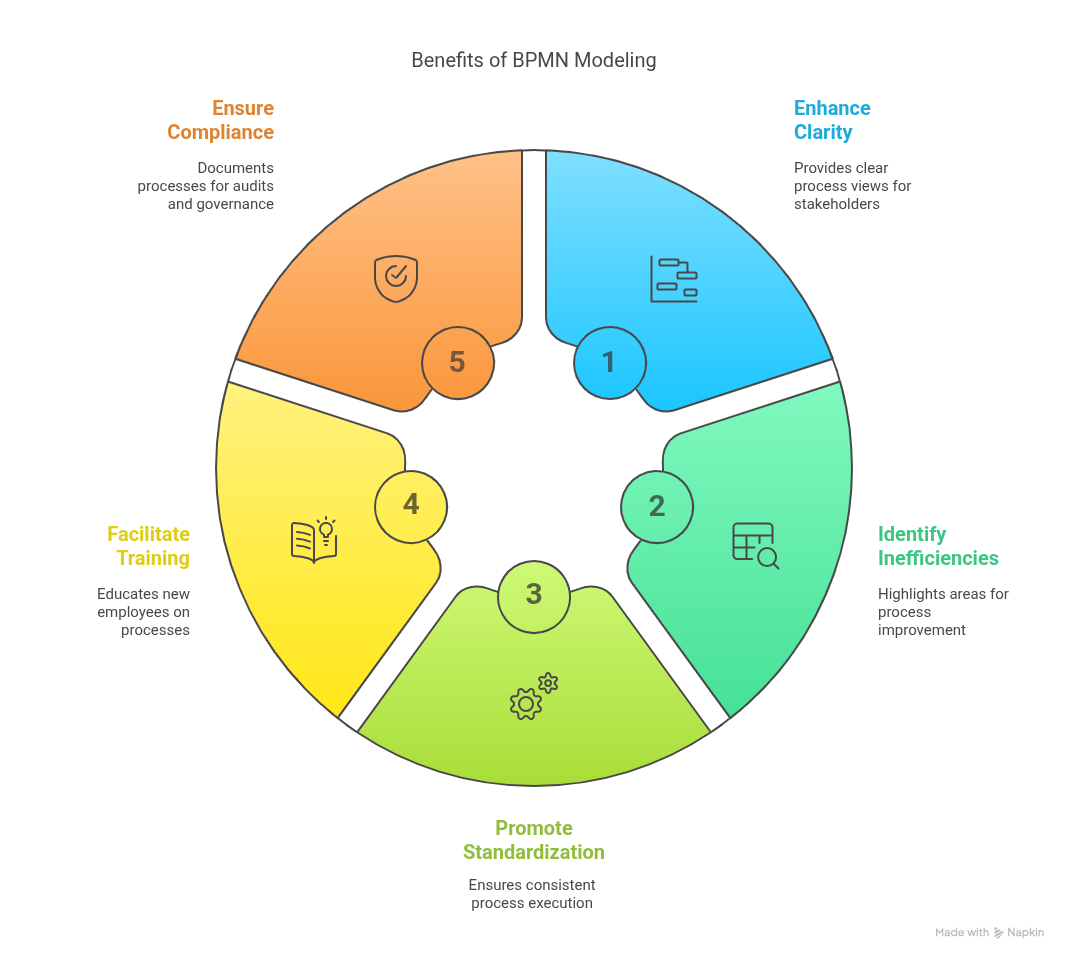
Business Process Modelling plays a vital role in building a culture of continuous improvement and operational clarity. By representing processes visually, it enables organizations to:
- 📊 Clarity and Transparency: Provide all stakeholders with a clear view of how processes work.
- 🔍 Process Improvement: Identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and opportunities for streamlining.
- 📏 Standardization: Promote consistent execution and quality across different teams and departments.
- 🎓 Training and Onboarding: Serve as a valuable tool for educating new employees.
- 🛡️ Compliance and Risk Management: Document processes for audits, regulations, and internal governance.
Common Techniques and Notations
There are various ways to model business processes, each with its own strengths. The most common notations include:
- BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation): This is the industry standard for detailed and expressive process diagrams. BPMN is favored for its clarity, consistency, and ability to bridge communication between business and technical teams. It allows for complex process modelling while remaining understandable to all stakeholders.
👉 Want to learn more? Read our article dedicated to BPMN notation and discover how it can enhance your process documentation. - Flowcharts: Ideal for illustrating simple sequences of actions. These are often used for internal documentation or initial drafts.
- Value Stream Mapping: A technique focused on identifying value-adding and wasteful steps, commonly applied in Lean methodologies.
While multiple notations are valid, BPMN stands out due to its structured semantics, wide adoption, and ability to support both manual and automated process execution.
👉 Already curious? Open a real BPMN diagram and see for yourself here.
Practical Applications of Business Process Modelling
Business Process Modelling is not a theoretical exercise—it has numerous practical applications that drive real business value. Among its most common uses:
- Process Mapping: Establishes a clear, shared understanding of current workflows and procedures, serving as the foundation for all other initiatives.
- Process Optimization: Helps streamline operations by identifying and eliminating waste, redundancies, and bottlenecks.
- Business Process Reengineering: Enables radical redesigns of core processes to achieve breakthrough improvements in performance and cost.
- Process Automation: Prepares processes for automation by detailing logic, actors, and decision paths in a clear and implementable manner.
- Digital Transformation: Supports the integration of modern technologies by aligning business operations with digital tools and platforms.
- Continuous Improvement: Encourages iterative refinement of processes through proven methodologies like Lean, Six Sigma, and Kaizen.
- Customer Journey Mapping: Allows organizations to visualize interactions from the customer’s perspective, identifying pain points and opportunities to enhance user experience.
Business Process Mapping
The goal of process mapping is to provide a simple yet comprehensive overview of how work is currently performed within an organization, identifying areas of inefficiency or confusion and paving the way for optimization and standardization. It also serves as an excellent communication tool for aligning teams and setting the groundwork for automation or reengineering initiatives.
🗺️ Want to learn how to create effective process maps? Read our step-by-step article on Business Process Mapping.
Examples of BPMN-Modeled Processes
Real BPMN models provide much more than pretty diagrams—they reveal the logic, clarify responsibilities, and simplify improvements. Let’s explore two real examples you can open and edit yourself!
1. Leave Request Process
This diagram presents a BPMN 2.0 model for managing employee vacation leave requests, ensuring a standardized, traceable, and efficient workflow. The process starts with the employee’s submission, moves through managerial approval and HR validation, includes required IT preparations, and addresses administrative tasks before, during, and after the leave period.

🔗 Open this process in the HEFLO modeler using a free account
2. Purchase Requisition Process
This process model defines the standardized approach for procuring goods and services across the organization. It covers the entire lifecycle—from the initial need identified by the requester to the final receipt of goods or completion of services—while accounting for scenarios like rejection or cancellation. Core principles include transparency, compliance with internal policies, thorough supplier validation, and end-to-end traceability of procurement actions.

🔗 Open this process in the HEFLO modeler using a free account
📚 Want more? Check out our library of BPMN-modeled processes and explore templates you can open directly in our modeler.
Conclusion
Business Process Modelling is not just about mapping tasks—it's about unlocking business agility, boosting operational excellence, and future-proofing your organization.
Whether your goal is automation, compliance, or customer experience enhancement, it all starts with a clear, well-modeled process.
🎯 Ready to start?
➡️ Create your free account and open our real BPMN diagrams now!
🎥 Want to see BPMN in action? Watch our free video class on BPMN modeling and learn how to create effective process diagrams step-by-step.